AI in Financial Services: Revolutionizing Banking and Investments

Artificial Intelligence is fundamentally transforming the banking industry, introducing efficiencies, enhancing customer experiences, and redefining operational frameworks. Banks, once synonymous with tradition and caution, are now evolving into agile, technology-driven institutions. The integration of AI is not merely an operational enhancement; it is a complete paradigm shift in how banks operate, interact with customers, and deliver value.
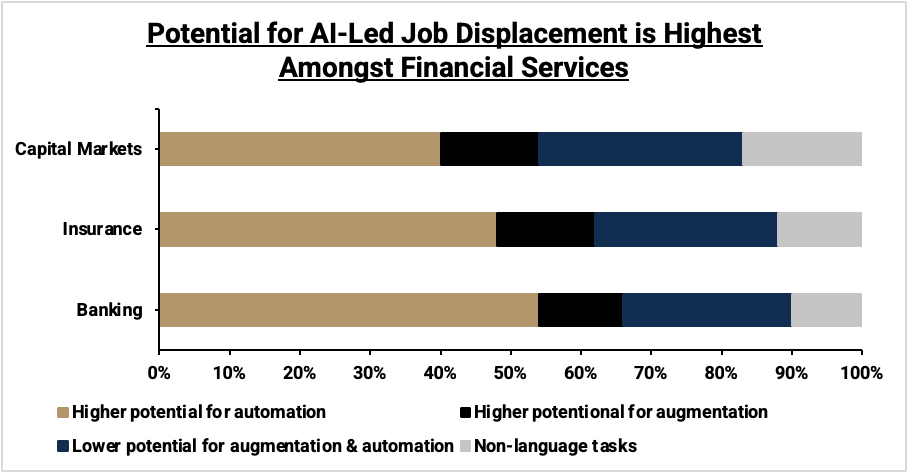
The financial sector's reliance on data makes it uniquely suited for AI adoption. According to a Citi TTS Client Survey, 93% of financial institutions believe AI will significantly boost profitability within five years. This optimism is grounded in AI's ability to transform core operations such as compliance, fraud detection, credit underwriting, and customer service. By 2028, the integration of AI is expected to add $170 billion to global banking profits, increasing the sector's total profit by 9%.
AI's Role in Redefining Banking
The applications of AI in banking are diverse, ranging from automating repetitive tasks to uncovering actionable insights in real-time. A key area of impact is customer engagement. AI-powered virtual assistants, such as Bank of America's "Erica," provide personalized, 24/7 customer support, resolving queries efficiently while simulating human-like interactions. These tools not only enhance customer satisfaction but also reduce operational costs by minimizing the need for large-scale customer service teams. Additionally, AI enables hyper-personalization, offering tailored financial advice, product recommendations, and loan options based on individual customer profiles.
Source: Citibank
Another critical application is fraud detection and transaction monitoring. The financial industry handles trillions of dollars in transactions annually, making it a prime target for fraudulent activities. AI algorithms excel in identifying anomalies within vast datasets, flagging potential risks in real-time. For example, HSBC employs AI systems that monitorover 680 million transactions annually, significantly reducing fraud-related losses.
Credit risk assessment and underwriting have also undergone significant advancements with AI. Traditional methods, which relied heavily on limited data points like credit scores, often excluded individuals with unconventional financial profiles. AI-driven systems, however, can analyze a broader range of data, including transactional history, social media behavior, and alternative credit metrics, allowing for more inclusive lending practices. Companies like Upstart are pioneers in this space, leveraging AI to expand credit access while maintaining robust risk management frameworks.
Despite these benefits, the integration of AI in banking is not without challenges. Legacy systems, which underpin 68% of banking operations, often act as barriers to seamless AI adoption. Modernizing these systems is both time-intensive and costly, with global banks projected to spend $120 billion on AI-related infrastructure upgrades in 2024 alone. Additionally, ethical concerns such as algorithmic bias and data privacy present significant governance challenges.
WealthTech: AI in Wealth Management
Beyond traditional banking, AI has made significant inroads into wealth management through the rise of WealthTech. WealthTech, a segment of fintech, uses AI, machine learning (ML), and blockchain to revolutionize how individuals and institutions manage wealth. The sector is growing rapidly, with Research and Markets projecting a compound annual growth rate of 14.7%, reaching $9.43 billion by 2028 from $4.72 billion in 2023.
The adoption of AI in wealth management is driven by the increasing demand for personalized, accessible financial solutions. Platforms like Charles Schwab's robo-advisory services illustrate how AI can provide low-cost, algorithm-driven investment management. Schwab, which boasts 35.7 million active brokerage accounts and $9.57 trillion in client assets as of mid-2024, exemplifies the transformative power of AI in delivering tailored financial advice at scale.
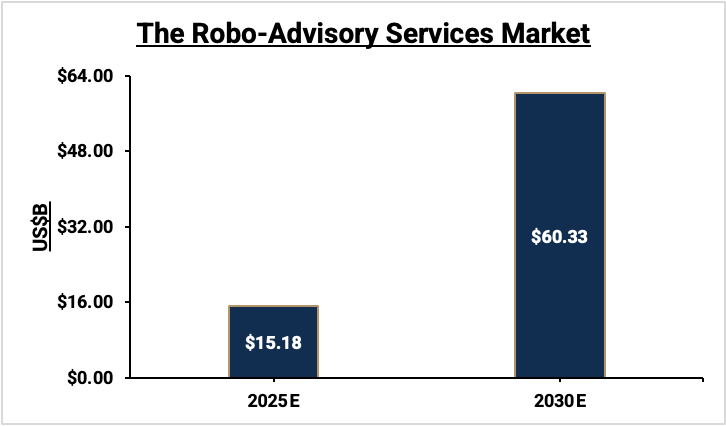
Robo-advisors are a cornerstone of WealthTech. These AI-powered platforms optimize portfolios, minimize risks, and offer tax-efficient investment strategies. According to Mordor Intelligence, the robo-advisory market is set to expand from $15.18 billion in 2025 to $60.33 billion by 2030, growing at an extraordinary CAGR of 31.78%. This explosive growth highlights the increasing consumer reliance on AI-driven tools for financial planning and investment.
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Generative AI and Its Expanding Role
Generative AI is poised to further revolutionize financial services by expanding the scope of AI applications. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on structured data, GenAI can analyze unstructured data—emails, transcripts, and reports—that constitute 80–90% of enterprise information. Its capabilities include generating text, summarizing data, and creating personalized financial content, making it a game-changer for investment research and portfolio management.
Investment research, a labor-intensive process, has significantly benefited from GenAI. Analysts now use AI to sift through extensive datasets, identify market trends, and generate comprehensive reports. According to Citi's Business Advisory Services, the integration of AI could save analysts up to 25% of their time, allowing them to focus on strategic decision-making. Moreover, AI-driven tools enhance portfolio optimization by analyzing historical data to predict future market conditions, enabling more accurate asset allocation strategies.
For example, in asset management, AI models like LASSO and neural networks are used to forecast returns and manage risks effectively. These tools help portfolio managers refine investment strategies, providing a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven market. Additionally, AI's ability to conduct back-testing of portfolios enables managers to evaluate various scenarios, ensuring optimal outcomes for clients.
AI's Economic and Operational Impacts
The economic implications of AI adoption extend beyond profitability. By automating routine processes, AI reduces operational costs and improves efficiency. A notable example is transaction monitoring, where AI systems handle millions of transactions daily, identifying suspicious activities with greater accuracy than human-led efforts. This operational efficiency translates into cost savings and enhanced risk management, key drivers of sector growth.
Furthermore, AI is reshaping internal banking operations. Large financial institutions, where 15–25% of the workforce is engaged in software and coding tasks, are using AI to streamline coding processes and accelerate development cycles. This reduces time-to-market for new financial products, enabling banks to stay competitive in a fast-evolving industry.
However, the benefits of AI are not evenly distributed. Digitally native firms, such as fintechs and big tech companies, are often faster adopters of AI than traditional banks weighed down by legacy infrastructure. This disparity creates competitive pressures, pushing incumbents to prioritize AI adoption to maintain market relevance.
The Future of AI in Financial Services
As AI continues to evolve, its role in financial services will only deepen. By 2030, autonomous AI agents could dominate financial transactions, using tokenized money and blockchain technologies to facilitate instant, secure settlements. These innovations promise to disrupt existing business models, creating new opportunities and challenges for financial institutions.
The proliferation of AI also necessitates robust governance frameworks. Issues like algorithmic transparency, data privacy, and ethical considerations must be addressed to maintain stakeholder trust. Additionally, regulatory bodies will need to adapt to the complexities introduced by AI, ensuring that innovation does not compromise compliance.
For financial institutions, the road ahead involves balancing innovation with responsibility. Investments in AI talent, infrastructure, and partnerships will be crucial for navigating this transformative era. Institutions that successfully integrate AI into their operations will not only enhance profitability but also redefine their roles in a rapidly changing financial landscape.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is no longer a supplementary tool for financial services; it is a transformative force redefining the industry. From automating banking operations and enhancing wealth management to driving innovation in investment research, AI is shaping a more efficient, inclusive, and dynamic financial ecosystem.
While challenges such as legacy systems and ethical concerns persist, the potential benefits far outweigh the risks. By embracing AI responsibly, financial institutions can unlock unprecedented value, delivering superior services to clients and achieving sustainable growth. As the financial sector adapts to this new reality, AI stands poised to become the defining technology of the decade, revolutionizing how money is managed, invested, and protected.